For a full description I would recommend;
| Color Atlas of THE HORSE'S FOOT Christopher C Pollitt Mosby Wolfe |
| EQUINE LAMINITIS - Dr Chris Pollit; for Rural Industries Research & Development Corporation Pub.No.01/129 |
| THE EQUINE DISTAL LIMB - Jean-Marie Denoix; An Atlas of Clinical Anatomy and Comparative Imaging, Manson Publishing |
The equine foot is an amazing structure that has to take the weight of the horse on a "finger nail". The weight passes down the bone column to the pedal bone that is suspended inside the hoof by the laminae.
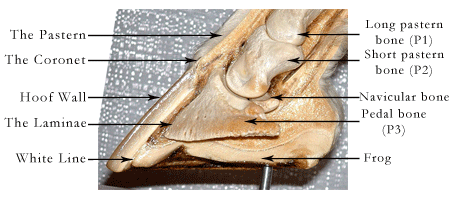
The inside of a hoof with the sensitive tissues and the bone removed.
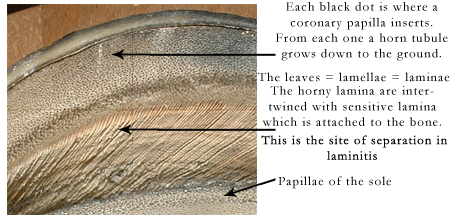
Close-up of inside the hoof wall.
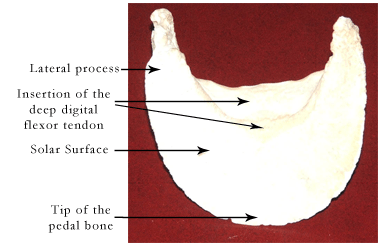
The pedal bone = the coffin bone = P3 = the distal phalanx
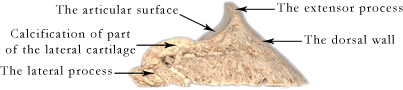
The ventral = palmar = solar surface of the pedal bone
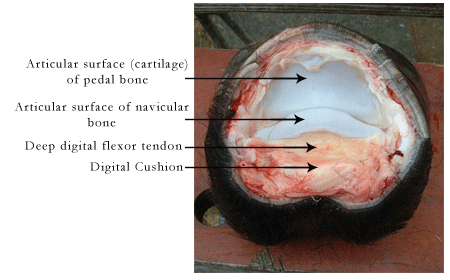
Disarticulation exposing the coffin joint.
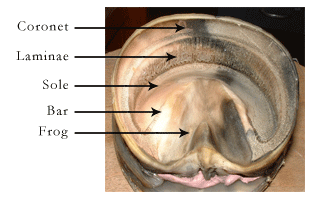
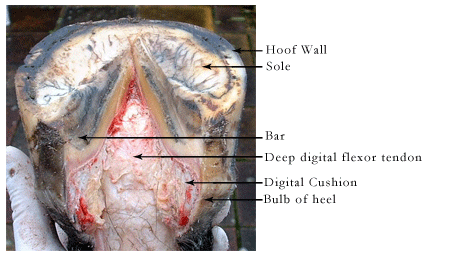
Solar surface of the hoof with the frog removed
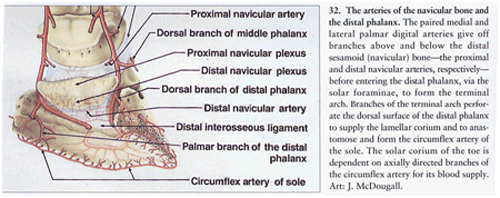
| The arterial supply of the navicular bone and the pedal bone (distal phalanx) |
| From "Color Atlas of The Horse’s Foot" Christopher C.Pollitt Mosby-Wolfe 1996 (Art J.McDougall) Page 22 |
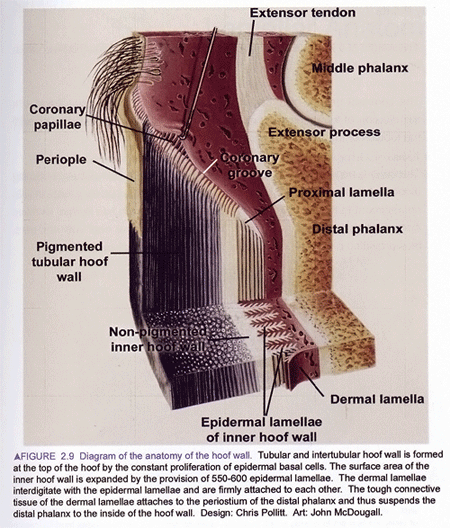
| The Anatomy of the Hoof Wall |
| From EQUINE LAMINITIS Dr Chris Pollit 2001 for Rural Industries Research & Development Corporation Pub.No.01/129 page 13 Art John McDougall |
Each primary lamella (lamina). has many secondary lamellae. The basement membrane lies between the secondary epidermal lamellae (of the hoof) and the secondary dermal lamellae. Breakdown at this site occurs in laminitis.
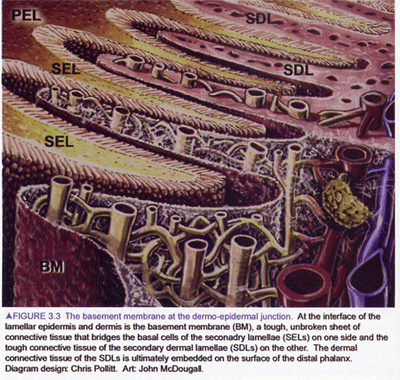
| From EQUINE LAMINITIS Dr Chris Pollit 2001 for Rural Industries Research & Development Corporation Pub.No.01/129 Page 18 Art John McDougall |